How Many Earths Fit in the Sun? 7 Astonishing Facts You Need to Know!
The Sun is the heart of our solar system, a colossal ball of fire that gives life to our planet. But have you ever wondered just how big the Sun really is compared to Earth? It’s a mind-blowing comparison, and in this blog, we’re diving into the numbers to answer a question that will leave you in awe: How many Earths can fit inside the Sun? Get ready to have your mind expanded with these 7 astonishing facts!

1. The Sun’s Immense Size: A Jaw-Dropping Comparison
To put it simply, the Sun is gigantic. Its diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers (864,000 miles), which is roughly 109 times wider than Earth’s diameter. But let’s break that down in a way that’s easier to visualize. Imagine lining up 109 Earths side by side—that’s how many would fit across the Sun’s diameter!
2. Earth’s Volume vs. The Sun’s Volume
Now, let’s talk volume. The Sun’s volume is so vast that it could fit approximately 1.3 million Earths inside it! Yes, you read that right—1.3 million! To put that into perspective, if Earth were the size of a marble, the Sun would be about the size of a large beach ball. That’s how massive the Sun is!
3. The Sun’s Mass: Holding the Solar System Together
While the Sun is incredibly large, it’s also unbelievably heavy. In fact, the Sun’s mass is about 333,000 times that of Earth. This immense mass gives the Sun a gravitational pull strong enough to keep all the planets in our solar system in orbit around it. Without the Sun’s gravitational force, the planets, including Earth, would drift off into space.
4. The Sun’s Core: The Powerhouse of Energy
The Sun isn’t just big; it’s also extremely powerful. At its core, the Sun produces energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of energy. This energy radiates outwards and eventually reaches Earth, providing the heat and light necessary for life. The core temperature of the Sun is a scorching 15 million degrees Celsius (27 million degrees Fahrenheit)!
5. The Sun’s Lifespan: Still Shining Bright
The Sun has been burning for about 4.6 billion years and is expected to continue for another 5 billion years. Throughout its life, the Sun will go through different phases, eventually expanding into a red giant and then shrinking into a white dwarf. But for now, it’s in a stable phase, continuing to shine brightly and support life on Earth.
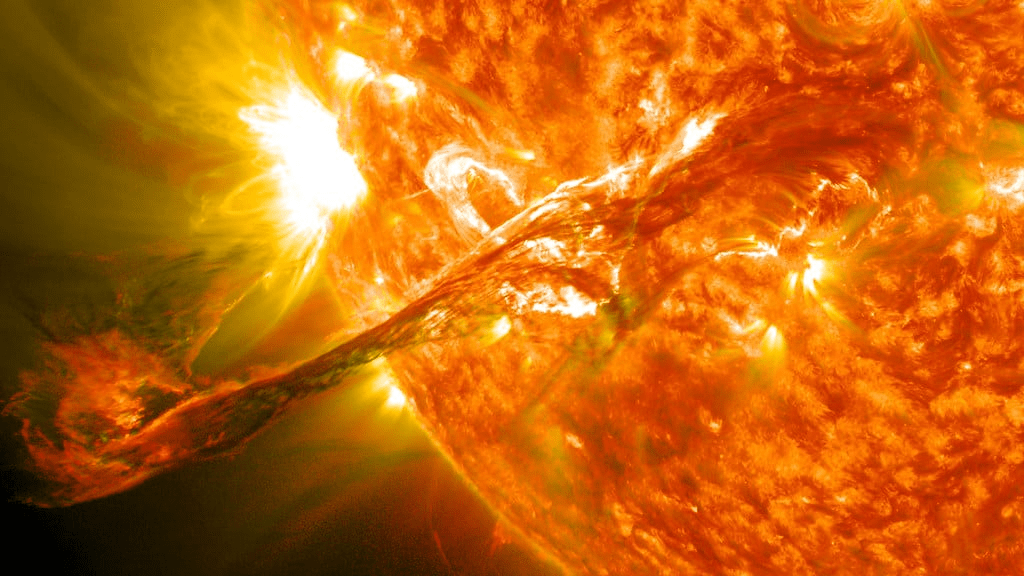
6. The Sun’s Rotation: A Slow and Steady Spin
Unlike Earth, which rotates on its axis once every 24 hours, the Sun takes much longer to complete one rotation. At its equator, the Sun rotates once every 25 days, while at its poles, it rotates once every 35 days. This difference in rotation speed is due to the Sun being a gaseous body, unlike the solid Earth.
7. The Sun’s Influence: The Solar Wind and Earth’s Magnetosphere
The Sun’s influence extends far beyond its physical size. It constantly emits a stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. This solar wind interacts with Earth’s magnetic field, creating stunning auroras and protecting us from harmful cosmic radiation. The Sun’s activity also affects space weather, which can impact satellite communications and even power grids on Earth.
8. The Sun’s Layers: A Deep Dive into Its Structure
The Sun isn’t just a single, uniform ball of gas. It’s composed of several layers, each playing a crucial role in how the Sun functions. Starting from the core, where nuclear fusion occurs, we move outward to the radiative zone, where energy slowly moves outward through radiation. Then there’s the convective zone, where hot plasma rises and cools as it nears the surface, creating a churning motion. The outermost layers include the photosphere (which we see as the Sun’s surface), the chromosphere, and the corona, which extends far into space and is visible during a solar eclipse.
9. The Sun’s Magnetic Field: The Source of Solar Flares and Sunspots
The Sun’s magnetic field is incredibly complex and much stronger than Earth’s. This magnetic field drives solar activity, including solar flares and sunspots. Sunspots are cooler, darker areas on the Sun’s surface caused by magnetic field disturbances. Solar flares, on the other hand, are sudden eruptions of energy that can send charged particles flying into space, sometimes reaching Earth and causing geomagnetic storms. These phenomena are not just fascinating—they can also have real-world effects, like disrupting communications and power systems on Earth.
10. The Sun’s Influence on Earth’s Climate
The Sun is the primary driver of Earth’s climate. The energy it emits in the form of sunlight heats our planet, driving weather patterns and ocean currents. Over time, variations in the Sun’s output can influence Earth’s climate. For example, periods of lower solar activity, like the Maunder Minimum in the 17th century, have been linked to cooler global temperatures. Understanding the Sun’s influence on our climate is crucial for scientists studying long-term climate change and its impacts on Earth.
11. The Future of the Sun: What Happens When It Runs Out of Fuel?
While the Sun has been shining for billions of years, it won’t last forever. As it burns through its hydrogen fuel, the Sun will eventually enter the red giant phase, expanding to many times its current size. This expansion will engulf the inner planets, possibly including Earth. After shedding its outer layers, the Sun will shrink into a white dwarf, a small, dense remnant of its former self. This process will take billions of years, so there’s no need to worry—our Sun still has a long life ahead of it!
12. The Sun’s Role in the Bigger Picture: Our Solar System’s Anchor
The Sun is the anchor of our solar system, holding all eight planets, their moons, and countless other objects in its gravitational grasp. Without the Sun’s immense gravity, our solar system as we know it wouldn’t exist. The Sun’s presence is also vital for the stability of our orbits, ensuring that Earth remains in the “Goldilocks zone,” where conditions are just right for liquid water—and life—to exist.

13. Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Humans have long recognized the potential of the Sun as an energy source. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that can be harnessed using solar panels to generate electricity. As technology advances, solar energy is becoming more efficient and widespread, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. The Sun’s energy is literally the power behind life on Earth, and now it’s helping to power our homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
14. The Sun and Timekeeping: How Our Ancestors Used It to Measure Time
Before the advent of modern clocks, people relied heavily on the Sun to track the passage of time. The position of the Sun in the sky determined everything from the hours of the day to the changing seasons. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Mayans, built structures aligned with the Sun’s movements, using its predictable path to create early calendars. Even today, we still use solar time in the form of time zones and the concept of noon when the Sun is at its highest point in the sky.
15. The Sun’s Impact on Technology: Solar Storms and Their Effects on Earth
While the Sun provides us with essential energy, it also has the power to disrupt our technology. Solar storms, caused by eruptions on the Sun’s surface, send waves of charged particles hurtling through space. When these particles reach Earth, they can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and even power grids. The famous Carrington Event of 1859 was a massive solar storm that caused widespread telegraph outages and even set some equipment on fire. Understanding and preparing for such solar events is crucial in our increasingly technology-dependent world.
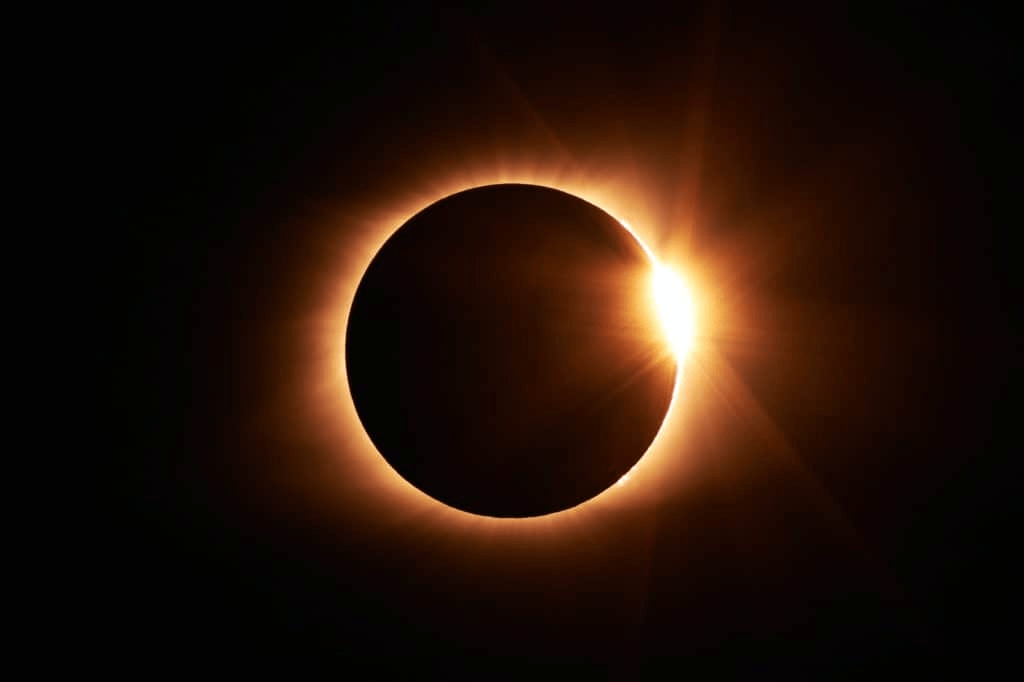
16. Solar Eclipses: The Rare Spectacles That Mesmerize the World
Solar eclipses are among the most awe-inspiring events that occur due to the Sun. During a solar eclipse, the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily blocking out the Sun’s light. These events have fascinated humans for millennia, often seen as omens or celestial wonders. Today, people travel across the globe to witness total solar eclipses, where day briefly turns into night. These rare occurrences remind us of the intricate dance between the Earth, Moon, and Sun that governs our sky.
17. The Sun’s Influence on Space Exploration: Powering Missions Beyond Earth
The Sun isn’t just a source of energy for life on Earth—it’s also a vital resource for space exploration. Solar panels power many spacecraft, from satellites orbiting Earth to missions venturing into deep space. NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, for example, is currently exploring the Sun’s outer atmosphere, gathering data that could help us understand solar winds and space weather. As we push further into the cosmos, the Sun will continue to be an essential partner in our journey.
18. The Cultural Significance of the Sun: From Worship to Inspiration
Throughout history, the Sun has held a significant place in human culture. Many ancient civilizations worshipped the Sun as a deity, recognizing its crucial role in sustaining life. The Sun has inspired countless myths, stories, and artistic creations, symbolizing everything from power and vitality to rebirth and enlightenment. In literature, art, and music, the Sun often represents hope, warmth, and life-giving energy. Its influence permeates our culture, reminding us of our deep connection to this celestial body.

19. The Future of Solar Power: Advancements in Technology and Sustainability
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, solar power is at the forefront of this transition. Technological advancements are making solar panels more efficient, affordable, and accessible than ever before. Innovations like solar roofs, solar farms, and even solar-powered vehicles are paving the way for a more sustainable future. The Sun’s energy is abundant and clean, offering a solution to the pressing challenge of climate change. As we continue to harness the Sun’s power, we move closer to a world that thrives on sustainable energy.
20. The Sun’s Enduring Mystery: What We Still Don’t Know
Despite all we’ve learned about the Sun, it remains a source of mystery and intrigue. Scientists continue to study the Sun’s behavior, seeking to understand phenomena like sunspots, solar flares, and the corona’s extreme temperature. Questions about the Sun’s influence on the solar system and its future evolution drive ongoing research. The Sun may be a familiar presence in our lives, but it still holds secrets that could change our understanding of the universe.
Conclusion: Embracing the Sun’s Power and Potential
The Sun is far more than just the star at the center of our solar system—it’s a source of life, energy, and inspiration. From the staggering number of Earths that could fit inside it to its crucial role in shaping our climate and powering our technology, the Sun’s influence is vast and enduring. By continuing to explore and understand the Sun, we not only satisfy our curiosity but also unlock new possibilities for harnessing its power in ways that benefit our planet and future generations.
Final Thought: How Will You Harness the Power of the Sun?
Whether it’s through solar energy, space exploration, or simply appreciating a beautiful sunrise, the Sun offers endless opportunities to enrich our lives. How will you connect with the Sun’s power? Share your ideas and experiences in the comments below, and let’s inspire each other to make the most of this incredible resource!

